As professional services industries continue to lean into technological innovation, smart contracts are emerging as a groundbreaking instrument with the potential to revolutionize traditional legal methodologies. With blockchain technology gaining momentum, smart contracts are garnering widespread attention for their efficacy, transparency, and security.
Deciphering Smart Contracts
At its essence, a smart contract is a self-executing agreement with its terms encoded directly into code. These contracts operate on blockchain technology, a decentralized ledger that ensures transparency and eliminates the necessity for intermediaries. Unlike conventional contracts, which rely on human interpretation and enforcement, smart contracts automatically execute and enforce themselves when specific conditions are met.
Smart contracts function on the principle of “if-then” logic, where actions are triggered based on predetermined criteria. For instance, in a real estate transaction, a smart contract may automatically transfer property ownership to the buyer upon receipt of payment, thereby obviating the need for escrow services and mitigating the risk of fraud or contention.
The Mechanics of Smart Contracts
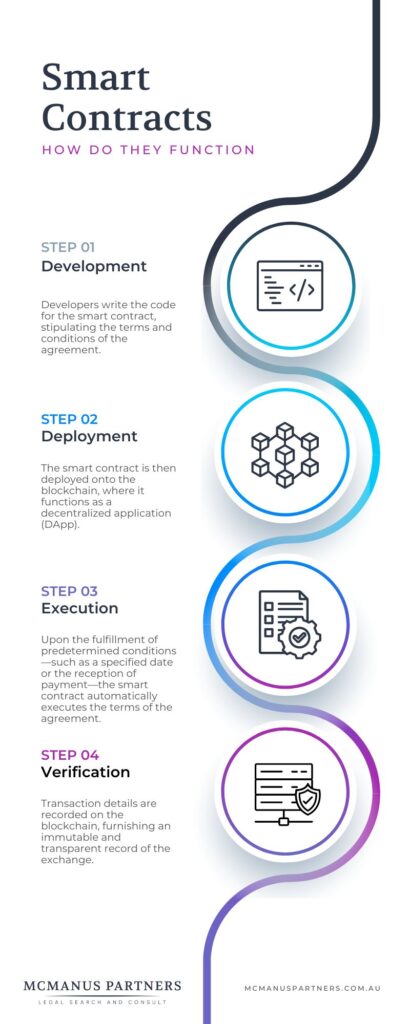
Smart contracts are crafted using programming languages tailored for blockchain platforms. Once deployed onto the blockchain, smart contracts become immutable, meaning their code cannot be altered or tampered with.
And for those of us that are not tech gurus, what is a blockchain exactly? In simple terms, a blockchain is like a digital ledger or record book that stores information across a network of computers. Imagine it as a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions or data. These blocks are linked together and secured using cryptography, making it extremely difficult to alter or tamper with the information stored within them.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of how smart contracts function:
Opportunities for Legal Professionals
For legal professionals, smart contracts present a plethora of opportunities to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, increase accuracy and security, and elevate client service. Here are several key areas where smart contracts can augment legal practices:
- Automation of Mundane Tasks:
Automate routine legal tasks such as contract drafting, review, and execution, thereby affording lawyers more time to concentrate on intricate matters. - Augmented Security and Transparency:
Blockchain technology ensures that smart contracts are tamper-proof and transparent, thereby diminishing the likelihood of fraud and disputes. Lawyers can leverage this technology to furnish clients with greater confidence and security in their transactions. - Cost Reduction:
By eliminating intermediaries and manual interventions, smart contracts can substantially reduce transaction costs associated with legal processes, rendering legal services more accessible to a broader spectrum of clients. - Expedited Dispute Resolution:
Smart contracts can encompass pre-defined dispute resolution mechanisms, enabling parties to resolve conflicts more efficiently without resorting to expensive litigation. - Diversification of Legal Services:
Smart contracts pave the way for new avenues in legal services, such as asset tokenization, decentralized finance (DeFi), and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), thereby enabling lawyers to diversify their areas of practice.
Examples of Smart Contract Application in Corporate and Commercial Law
Supply Chain Management:
Streamline supply chain management by automating processes such as procurement, logistics, and payments. For instance, in a manufacturing company, a smart contract can be utilized to automatically trigger orders for raw materials when inventory levels reach a certain threshold. Additionally, smart contracts can facilitate real-time tracking of shipments and automatically release payment to suppliers upon delivery confirmation, thereby reducing administrative overhead and mitigating disputes.
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A):
In the realm of M&A transactions, smart contracts can simplify and expedite the negotiation and execution of agreements between parties. For example, a smart contract can be employed to automate the due diligence process by securely storing and sharing relevant documents on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and confidentiality. Moreover, smart contracts can facilitate the escrow of funds and the transfer of assets upon the fulfilment of predetermined conditions, streamlining the closing process and reducing transactional costs.
Intellectual Property (IP) Rights Management:
Smart contracts can revolutionize the management of intellectual property rights by providing a secure and transparent platform for the registration, licensing, and enforcement of patents, trademarks, and copyrights. For instance, a smart contract can be utilized to automate royalty payments to content creators or musicians based on the usage of their intellectual property. Additionally, smart contracts can enable the creation of decentralized marketplaces for buying, selling, and licensing intellectual property rights, fostering innovation and fair compensation for creators.
McManus Partners consult with leading Australian legal practices around recruitment, firm growth, team coaching and development opportunities. The technology development space is often discussed as a top lever for firms and in attracting legal talent. To discuss consultation with your firm on market benchmarks in this space, or other development opportunities, feel free to Contact Us. Likewise as an individual lawyer, if you are looking to assess firms at the forefront of this transformation for your next career move, we are available for a confidential consult.


